Cơ bản về Reactor và Reactive API WebFlux
Reactive Stream được bắt đầu phát triển từ 2013 nó ra đời với mục đích cung cấp một chuẩn cho việc xử lý các luồng bất đồng bộ (asynchronous stream processing) với một ưu điểm không bị tắc (nonblocking backpressure).
Đặc tả của Reactive Stream có thể được thể hiện qua 4 interface chính
- Publisher
- Subscriber
- Subscription
- Processor
Mọi người tìm hiểu thêm về các interface này qua các kênh khác nhau.
Trong Reactive Stream có 2 kiểu lõi Mono và Flux, được coi là implement cho Publisher interface. Là nguồn cung cấp dữ liệu cho stream.
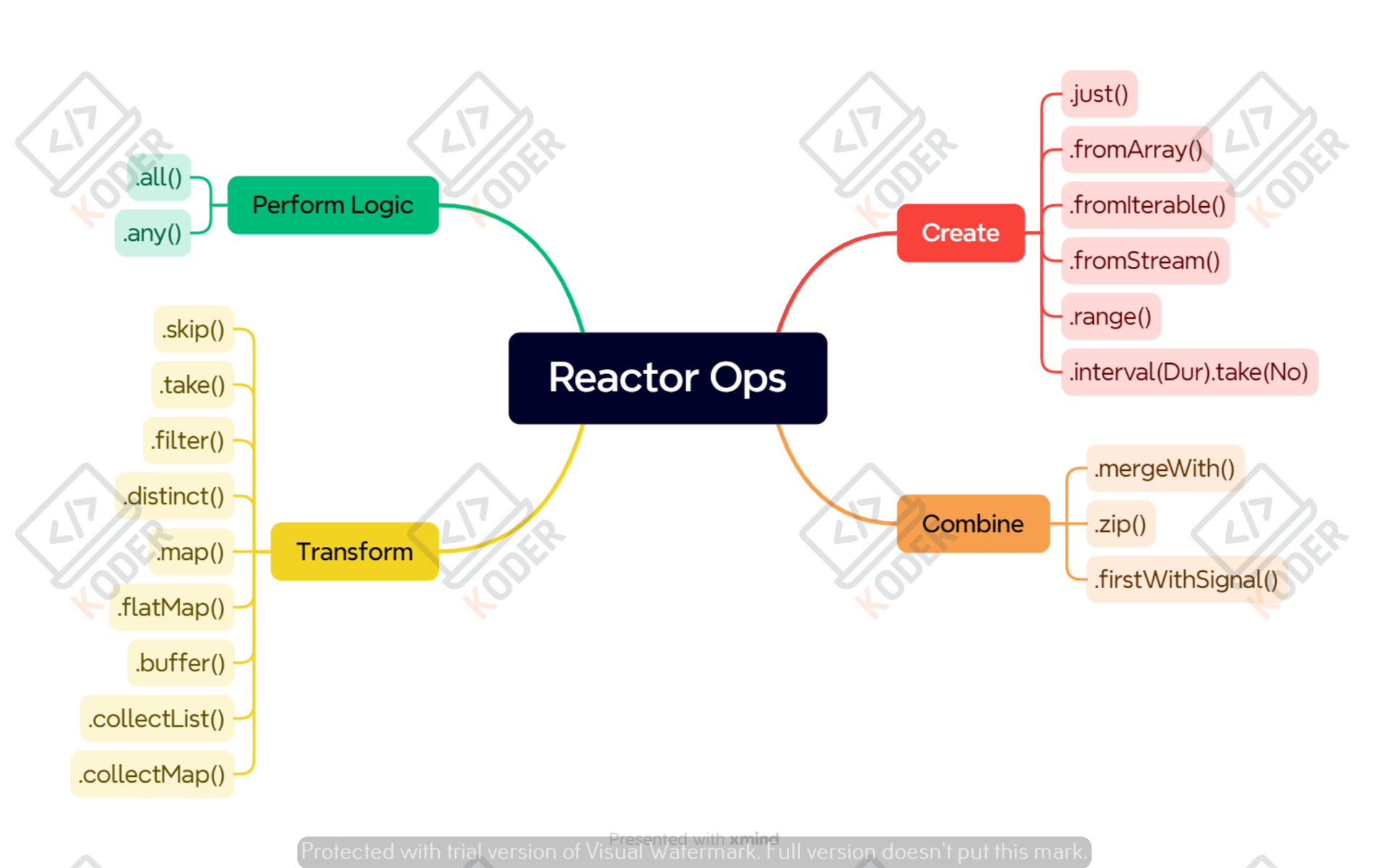
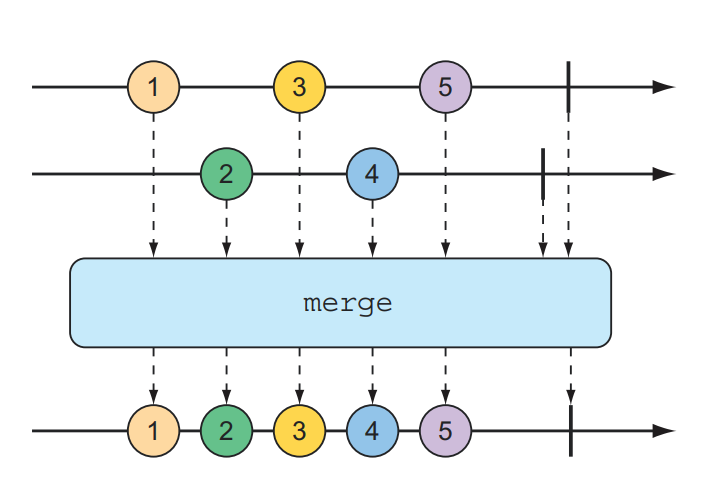
Biểu đồ Marble thể hiện luồng dữ liệu nguồn, toán tử tác động và kết quả của một stream, mọi người cần tìm hiểu qua về loại biểu đồ này.
Flux thể hiện cho luồng dữ liệu có thể có 0 phần tử, 1 phần từ hoặc nhiều (không giới hạn)
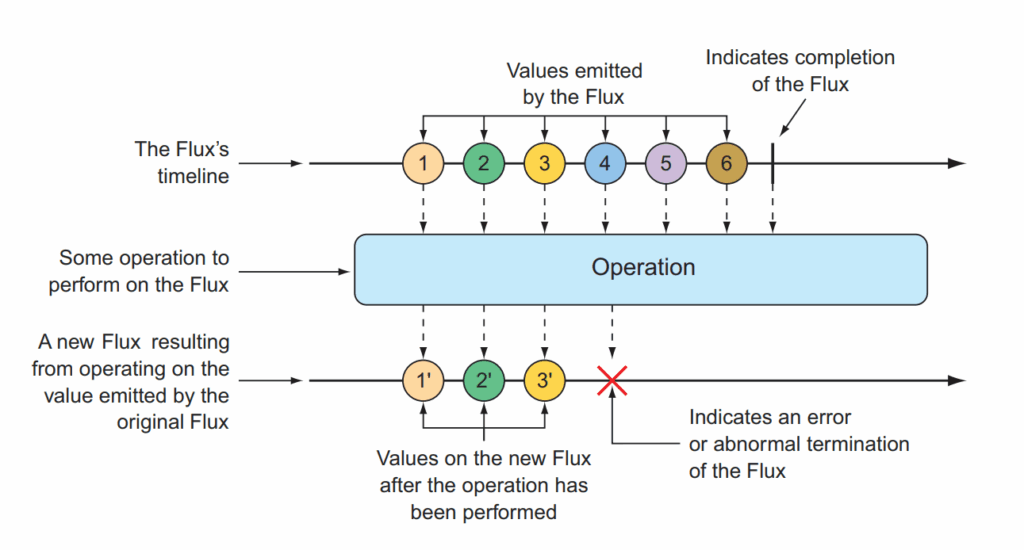
Mono thể hiện cho dữ liệu có thể là 0 phần tử hoặc không nhiều hơn 1 phần tử
Để tử dụng Reactor trong Spring Boot ta cần khai báo
<dependency>
<groupId>io.projectreactor</groupId>
<artifactId>reactor-core</artifactId>
</dependency>Các toán tử (operations) trong reactive
Có khoảng 500 toán tử (ops) trong Flux và Mono, anh em nào làm sâu về reactive cần thời gian để tìm hiểu từng toán tử, bài viết này chỉ liệt kê ra một số nhóm và đại diện toán tử hay dùng của mỗi nhóm, trong bài hướng dẫn tạo RESTful API với Reactive mình sẽ show thêm các toán tử hay dùng trong dự án.
Với sự hỗ trợ AI, có thể mọi người không cần nhớ toàn bộ, có thể đưa ra một số gợi ý AI sẽ giúp chúng ta sử dụng các toán tử một cách hợp lý trong ngữ cảnh được cung cấp.
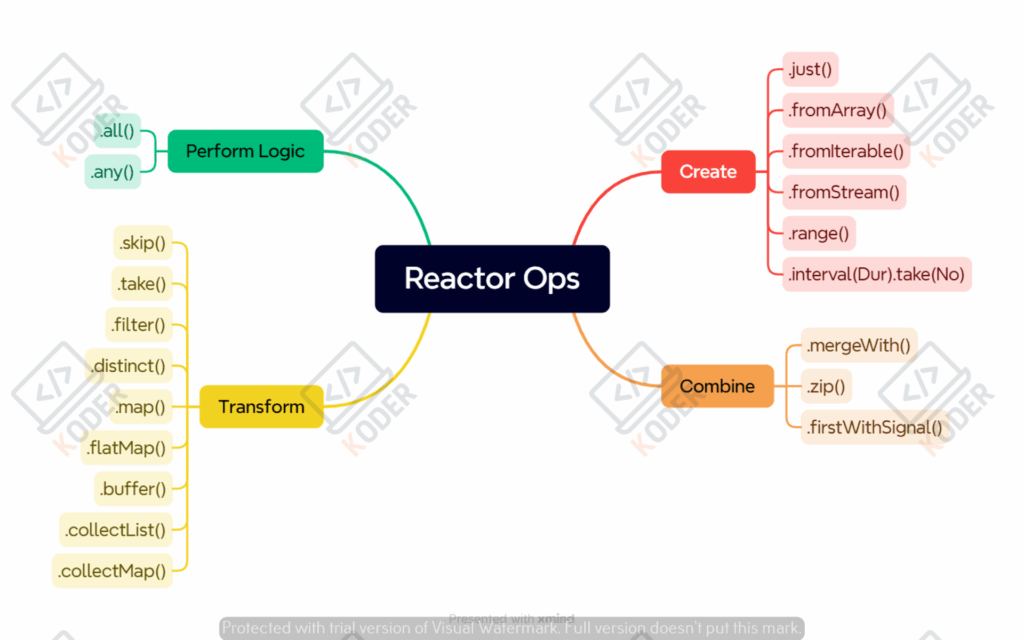
Thực hành với các toán tử cơ bản giúp chúng ta hiểu rõ hơn về cách Reactive hoạt động, là cơ sở tốt để áp dụng một cách tối ưu khi kết hợp các toán tử khác nhau để giải quyết bài toán thự tế.
Các thực hành các toán tử trên, bạn có thể sử dụng AI hỗ trợ và sử dụng công cụ test StepVerifier của reactive để xác minh hoạt động của toán tử.
Đây là một ví dụ về toán tử merge, được minh họa qua biểu đồ Marble và implement trong Java code
@Test
public void mergeFluxes() {
Flux<String> characterFlux = Flux
.just("Garfield", "Kojak", "Barbossa")
.delayElements(Duration.ofMillis(500));
Flux<String> foodFlux = Flux
.just("Lasagna", "Lollipops", "Apples")
.delaySubscription(Duration.ofMillis(250))
.delayElements(Duration.ofMillis(500));
Flux<String> mergedFlux = characterFlux.mergeWith(foodFlux);
StepVerifier.create(mergedFlux)
.expectNext("Garfield")
.expectNext("Lasagna")
.expectNext("Kojak")
.expectNext("Lollipops")
.expectNext("Barbossa")
.expectNext("Apples")
.verifyComplete();
}Xây dựng RESTful APIs với WebFlux
Reactive web có điểm cộng là xử lý được nhiều request đổng thời và và không bị ‘tắc’, để vận hành được cơ chế này nó sử dụng một kỹ thuật là event looping, được minh họa như sau
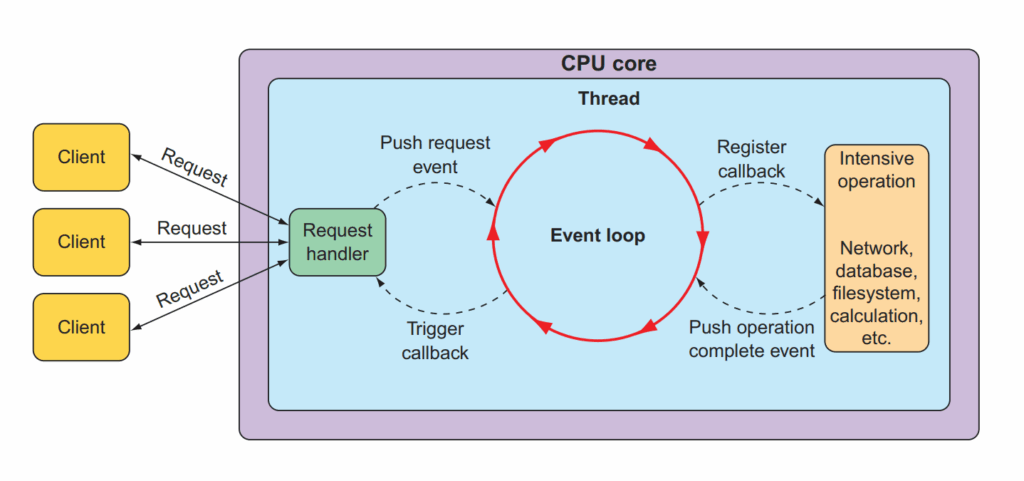
Trong event loop mọi thử được điều khiển (handled) như một sự kiện, khi một hành động cần-nhiều-thời-gian-để-xử-lý (Intensive operation) (ví dụ: lưu trữ datbase, lưu file, gọi dịch vụ qua mạng, v.v..) event loop sẽ đăng ký callback cho hành động đó có thể thực hiện song song (parallel), trong khi đó nó sẽ đi thực hiện xử lý event khác (ngày khi đăng ký callback xong chứ không đợi đến khi hành động đó được thực hiện xong).
Sau khi hành động thực hiện xong nó sẽ báo lại event loop và trigger callback trả dữ liệu cho request ban đầu.
Spring đề xuất một web framework cho reactive web là Spring WebFlux.
WebFlux là framework tồn tại song song với Spring MVC mà chúng ta đã quen dùng, Spring MVC xử lý các request theo hướng synchronous, việc dùng asynchronous và dùng synchronous cái nào tốt hơn mình không bàn luận ở đây vì nó là một phạm trù rộng. Cách xây dựng RESTful API mình đã giới thiệu ở bài trước, trong bài này mình sẽ hướng dẫn xây dựng RESTful trên Reactive WebFlux.
Để một ứng dụng reactive phát huy được lợi thế của nó là nonblocking thì yêu cầu toàn bộ service tham gia vào luồng xử lý cần phải hộ trợ reactive. Ta xem hình minh họa dưới đây.
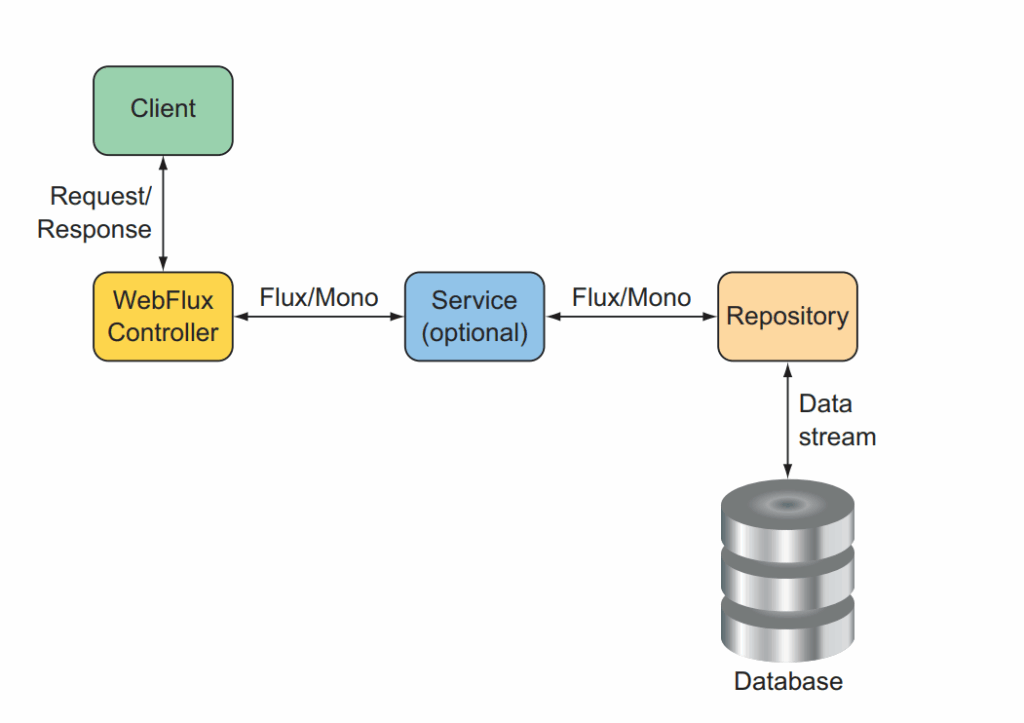
Nếu như tầng database không hỗ trợ reactive operation, tức là request sẽ bị block tại database, nó sẽ phá vỡ kiến trúc nonblocking của reactive, để giải quyết vấn đề này ban đầu các adaptor hỗ trợ các database được viết để đảm bảo kết nối đến datbase sẽ là reactive. Với những phiên bản Spring Boot 3.x thì hầu như các database, lưu trữ file S3, hay gọi các restful service khác đều đã hỗ trợ reactive, do vậy không cần kết nối qua adaptor. Mình sẽ có một bài viết giới thiệu cách kết nối đến: DB: Postgres, Mongo, Redis, Elasticsearch hay lưu file AMZ S3 sử dụng reactive.
Phần lý thuyết và reactive mình chỉ tóm tắt những phần quan trọng, các bạn mới làm việc với reactive cần đọc và thực hành thêm tại các nguồn khác nhau để có được kiến thức cơ bản trước.
[Hands-on] Thực hành xây dựng RESTful với WebFlux
Mã nguồn của phần hands-on mọi người tham khảo
Trong project này chúng ta cũng sử dụng kiến trúc phân lớp như trong project sử dụng Spring MVC
Giả sửa yêu cầu xây dựng API lưu sản đối tượng Sản phầm (product), với các đặc tả OpenAPi sau
openapi: "3.1.0"
info:
title: OpenAPI definition
version: v0
servers:
- url: http://localhost:8080
description: Generated server url
paths:
/api/v1/products:
post:
tags:
- product-controller
operationId: addProduct
parameters:
- name: command
in: query
required: true
schema:
$ref: "#/components/schemas/ProductCommand"
responses:
"200":
description: OK
content:
"*/*":
schema:
$ref: "#/components/schemas/ProductResponse"
components:
schemas:
ProductCommand:
type: object
properties:
uuid:
type: string
name:
type: string
description:
type: string
price:
type: number
stockQuantity:
type: integer
format: int32
ProductResponse:
type: object
properties:
uuid:
type: string
name:
type: string
description:
type: string
price:
type: number
stockQuantity:
type: integer
format: int32
createdAt:
type: string
format: date-time
updatedAt:
type: string
format: date-timeCác thư viện cần thiết
Khi khai báo sử dụng starter webflux web-server sẽ chuyển sang sử dụng là Netty thay vì Tomcat như Spring MVC.
spring-boot-starter-data-r2dbc là thư viện hỗ trợ Reactive cho database, r2dbc-postgresql là thư viện để sử dụng Postgres, nếu sử dụng các database khác ta sử dụng thư viện tương ứng
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-webflux'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-r2dbc'
runtimeOnly 'org.postgresql:r2dbc-postgresql'Validator
Trong lớp validator của Reactive ta thấy có một chút thay đổi so với Spring MVC
- Trả về
Mono<Void>thay vìvoid, khi toàn bộ các hàm validate hoàn thành và không có lỗi sẽ trả vềMono.empty(). - Trả về một exception trong WebFlux sẽ dùng
Mono.error(), cách để bắt exption này cũng có phần khác Spring MVC, mình sẽ trình bày ở phần khác. .then()là một toán tử gọi liên tiếp (chains) các reactive method khác.
Validator sẽ được gọi bởi Controller, sau khi validate một đối tượng thành công nó sẽ gọi tiếp đến các service nghiệp vụ
public class ProductValidator {
public Mono<Void> validateSaveProductCommand(ProductCommand productCommand) {
return validateLength(productCommand.name(), 3, 256)
.then(validateSpecialCharacters(productCommand.name()))
.then(validateLength(productCommand.description(), 3, 5000))
.then(validatePrice(productCommand.price()))
.then(validateStockQuantity(productCommand.stockQuantity()))
.then(Mono.defer(() -> {
if (productCommand.uuid() != null) {
return validateUUID(productCommand.uuid());
}
return Mono.empty();
}));
}
private Mono<Void> validateSpecialCharacters(String value) {
if (value == null) {
return Mono.error(new NullPointerException("Value cannot be null"));
}
if (!value.matches("^[a-zA-Z0-9_\\- ]+$")) {
return Mono.error(new IllegalArgumentException(
"Value contains invalid characters. Only alphanumeric, underscore, hyphen, and space are allowed."));
}
return Mono.empty();
}
}DTO và Entity
Ta có thể sử dụng các POJO object thông thường trong Java, hoặc có thể sử dụng kiểu dữ liệu record trong Java cho safe-thread và immutable.
public record ProductCommand(String uuid,
String name,
String description,
BigDecimal price,
Integer stockQuantity
) {
//with UUID
public ProductCommand withUuid(String uuid) {
return new ProductCommand(uuid, name, description, price, stockQuantity);
}
}tương tự cho ProductResponse
Với entity ta cũng sử dụng record, ta để ý đến import ở đây Id và Table thuộc springframework chứ không thuộc jpa như trong Spring MVC
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.relational.core.mapping.Table;
@Table("products")
public record ProductEntity(
@Id
Long id,
String uuid,
String name,
String description,
BigDecimal price,
Integer stockQuantity,
Instant createdAt,
Instant updatedAt
) {
// Constructor with all fields
public ProductEntity(Long id,
String uuid,
String name,
String description,
BigDecimal price,
Integer stockQuantity,
Instant createdAt,
Instant updatedAt) {
this.id = id;
this.uuid = uuid;
this.name = name;
this.description = description;
this.price = price;
this.stockQuantity = stockQuantity;
this.createdAt = createdAt != null ? createdAt : Instant.now();
this.updatedAt = updatedAt != null ? updatedAt : Instant.now();
}
//with name
public ProductEntity withName(String name) {
return new ProductEntity(id, uuid, name, description, price, stockQuantity, createdAt, updatedAt);
}
//with description
public ProductEntity withDescription(String description) {
return new ProductEntity(id, uuid, name, description, price, stockQuantity, createdAt, updatedAt);
}
public ProductEntity withPrice(BigDecimal price) {
return new ProductEntity(id, uuid, name, description, price, stockQuantity, createdAt, updatedAt);
}
public ProductEntity withStockQuantity(Integer stockQuantity) {
return new ProductEntity(id, uuid, name, description, price, stockQuantity, createdAt, updatedAt);
}
//with updatedAt
public ProductEntity withUpdatedAt(Instant updatedAt) {
return new ProductEntity(id, uuid, name, description, price, stockQuantity, createdAt, updatedAt);
}
}Repository
Sẽ sử dụng Repository dành riêng cho Reactive ReactiveCrudRepository, khi dùng ReactiveCrudRepository các hàm build-in tương tự tên như trong JPA nhưng giá trị trả về theo kiểu Publisher trong reactive là Mono nếu là giá trị đơn, Flux nếu là một mảng
public interface ProductRepository extends ReactiveCrudRepository<ProductEntity, Long> {
Mono<ProductEntity> findByUuid(String uuid);
}Cầu hình database
Phần cấu hình database có khác so với Spring MVC, và sẽ được cấu hình như sau
spring:
r2dbc:
url: r2dbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/${DB_NAME}
username: ${DB_USERNAME}
password: ${DB_PASSWORD}
driver: postgresql
pool:
initial-size: 5
max-size: 20Mapping
Các class mapping tương tự như Spring MVC, đầu vào dữ liệu là đối tượng Java thuần không phải reactive, vì hành động mapping ở đây khi chuyển qua lại giữa ProductCommand -> ProductEntry và ProductEntry -> ProductResponse không phải là hành động intensive operation.
public class ProductMapper {
public ProductEntity toEntity(ProductCommand command) {
if (command == null) {
return null;
}
return new ProductEntity(
null, // id will be generated by the database
command.uuid(),
command.name(),
command.description(),
command.price(),
command.stockQuantity(),
null, // createdAt will be set to current time in the entity constructor
null // updatedAt will be set to current time in the entity constructor
);
}
}Service
Đây là lớp thực hiện logic nghiệp vụ của app, nhận đầu vào là ProductCommand lưu vào trong database, sau đó trả về ProductResponse tại đây nó sẽ gọi đến mapper để convert ProductCommand sang ProductEntry sau đó lưu và convert ProductEntry đã được lưu sang ProductResponse. Quá trình này được minh họa trong reactive bằng đoạn code sau đây
#1sẽ convert sang ProductEntry và lưu#2sau khi lưu giá trị nhận được ta gọi toán tửmapcủa reactor, và gọi hàm lambda function để map ProductEntry sang ProductResponse và trả về- các toán tử khác phục vụ việc retries và quản lý ngoại lệ mình sẽ nói ở một bài khác.
public class ProductService {
private final ProductRepository productRepository;
private final ProductMapper productMapper;
private final RetryUtil retryUtil;
public Mono<ProductResponse> saveProduct(ProductCommand command) {
return productRepository
.save(productMapper.toEntity(command)) //#1
.map(productMapper::toResponse) //#2
.as(mono -> retryUtil.applyRetry(mono, "save product", log))
.doOnError(error -> log.error("Error saving product: {}", error.getMessage()))
.onErrorMap(error -> new RuntimeException("Custom mapped exception", error))
.onErrorResume(error -> {
log.info("Fallback logic triggered");
return Mono.just(new ProductResponse(
"fallback-id",
"fallback-name",
"fallback-description",
BigDecimal.ZERO,
0,
Instant.now(),
Instant.now()
));
})
.onErrorReturn(new ProductResponse(
"default-id",
"default-name",
"default-description",
BigDecimal.ZERO,
0,
Instant.now(),
Instant.now()
));
}
}Controller
Nó sẽ implement endpoint, bằng việc gọi validator xem đầu vào hợp lệ không? sau đó gọi đến service để thực hiện lưu vào trong database.
public class ProductController {
private final ProductService productService;
private final ProductValidator productValidator;
@PostMapping("/api/v1/products")
public Mono<ResponseEntity<ProductResponse>> addProduct(ProductCommand command) {
return productValidator.validateSaveProductCommand(command).then(
productService.saveProduct(command)
.map(ResponseEntity::ok)
.onErrorResume(e -> {
log.error("Error adding product: {}", e.getMessage());
return Mono.just(ResponseEntity.status(500).build());
})
);
}
}Như vậy ta đã implement xong RESTful API bằng reactive, đây là mã nguồn mọi người có thể tham khảo.
Test APIs
Ta có thể sử dụng công cụ OpenAPI để test luôn trên trình duyệt
http://localhost:8080/openapi/swagger-ui/index.html#/product-controller/addProduct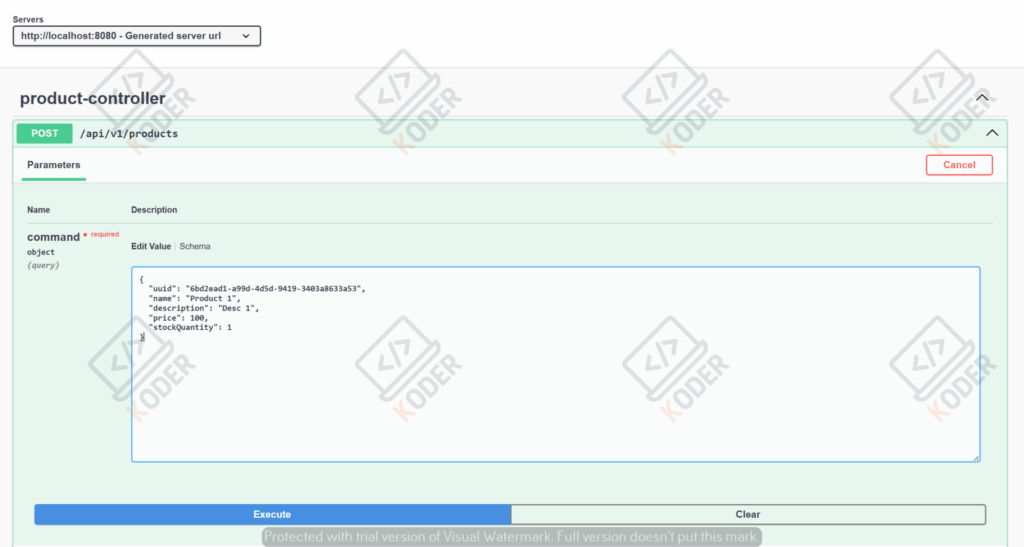
Đây là response ta nhận được
{
"uuid": "6bd2ead1-a99d-4d5d-9419-3403a8633a53",
"name": "Product 1",
"description": "Desc 1",
"price": 100,
"stockQuantity": 1,
"createdAt": "2025-07-25T09:26:56.484102800Z",
"updatedAt": "2025-07-25T09:26:56.484102800Z"
}Tổng kết
WebFlux là một implement cho Reactive Web với mục đích xây dựng được các web service có thể handle một lượng request lớn trong một tài nguyên (core CPU) hữu hạn bởi áp dụng kỹ thuật event looping. Với đặc điểm non-blocking của mình, khi triển khai hệ thống nếu áp dụng với các kỹ thuật khác như giảm áp, retires, đoản mạch nó sẽ là một công cụ hữu hiệu cho việc xử lý các điểm thắt cổ chai khi triển khai theo mô hình Spring MVC.
Các toán tử reactive có rất nhiều để kết hợp nhuần nhuyễn, hợp lý cần lập trình viên thực hành nhiều để có những giải pháp hay, luôn có một cách triển khai tối ưu hơn cho một bài toán cụ thể.
Sử dụng AI hỗ trợ khi viết code reactive là điều rất hiệu quả, AI có thể giúp ta đưa ra được các gợi ý sử dụng toán tử một cách hiệu quả.

Để lại một bình luận