Các thư viện hỗ trợ Reactive (Postgres, Mongo, Elasticseach, Redis, v.v…)
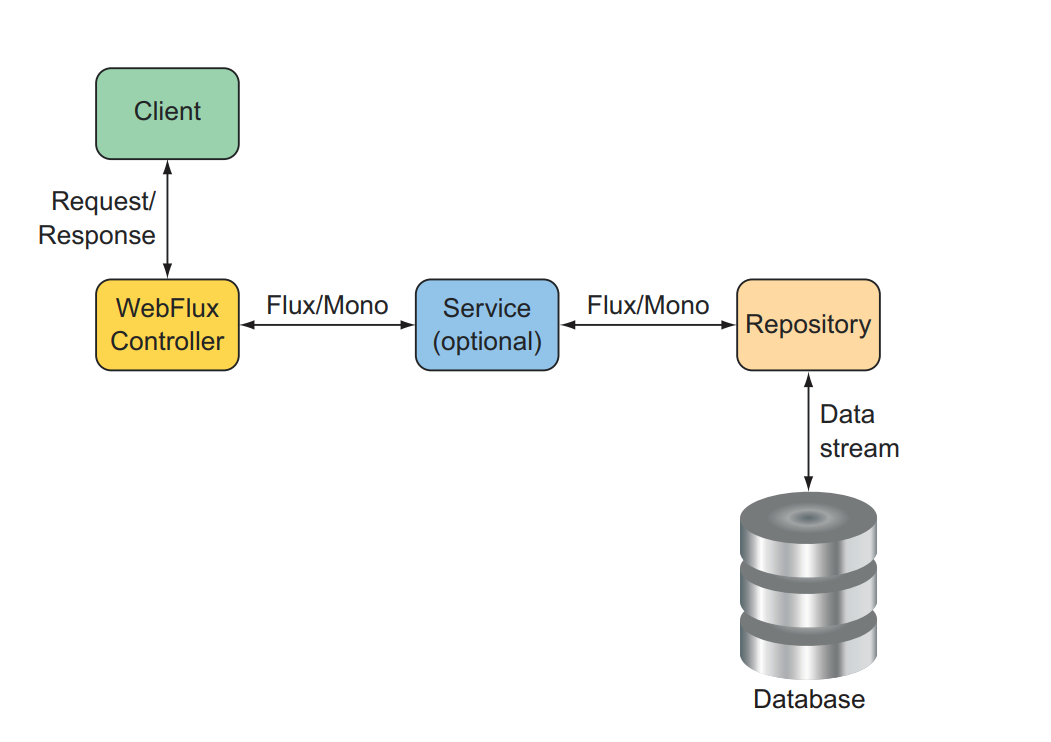
Để một ứng dụng reactive thể hiện được tính chất non-blocking thì yêu cầu các dịch vụ bên trong ứng dụng như: tương tác với cơ sở dữ liệu, gọi API, dịch vụ lưu trữ file v.v.. cũng cần có yêu cầu về bất đồng bộ.
Đây là bài tiếp theo trong chuối bài về Reactive, các bạn đọc thêm về 2 bài trước đó để hiểu thêm:
- Cơ bản về Reactive và RESTful API bằng WebFlux: https://koder.vn/2025/07/25/co-ban-ve-reactor-va-reactive-api-webflux/
- Xử lý ngoại lệ trong Reative: https://koder.vn/2025/07/26/quan-ly-ngoai-le-error-exception-handling-trong-reactive/
Ban đầu các thư viện dịch vụ trên chưa hỗ trợ reactive do vậy các adaptor được viết ra giúp app tương tác với các dịch vụ đó dưới dạng bất đồng bộ, nhưng với những phiên bản Spring Boot mới nhất, các thư viện dịch vụ trên đã hỗ trợ kết nối bất đồng bộ một cách native
Trong bài này mình sẽ hướng dẫn cấu hình kết nối đến các dịch vụ sau qua reactive
- Postgres database
- MongoDB
- Elasticsearch
- Redis
- Gọi HTTP request bằng reactive
- File upload (S3)
Postgres database
Trong bài trước ta đã biết cách cầu hình kết nối app với database Postgres thông qua cấu hình kế nối trong file YAML, đấy là trong trường hợp có 1 database, khi app có kết nối đến nhiều hơn 1 database ta không thể dùng cách cấu hình này được, mà cần tạo file cấu hình database.
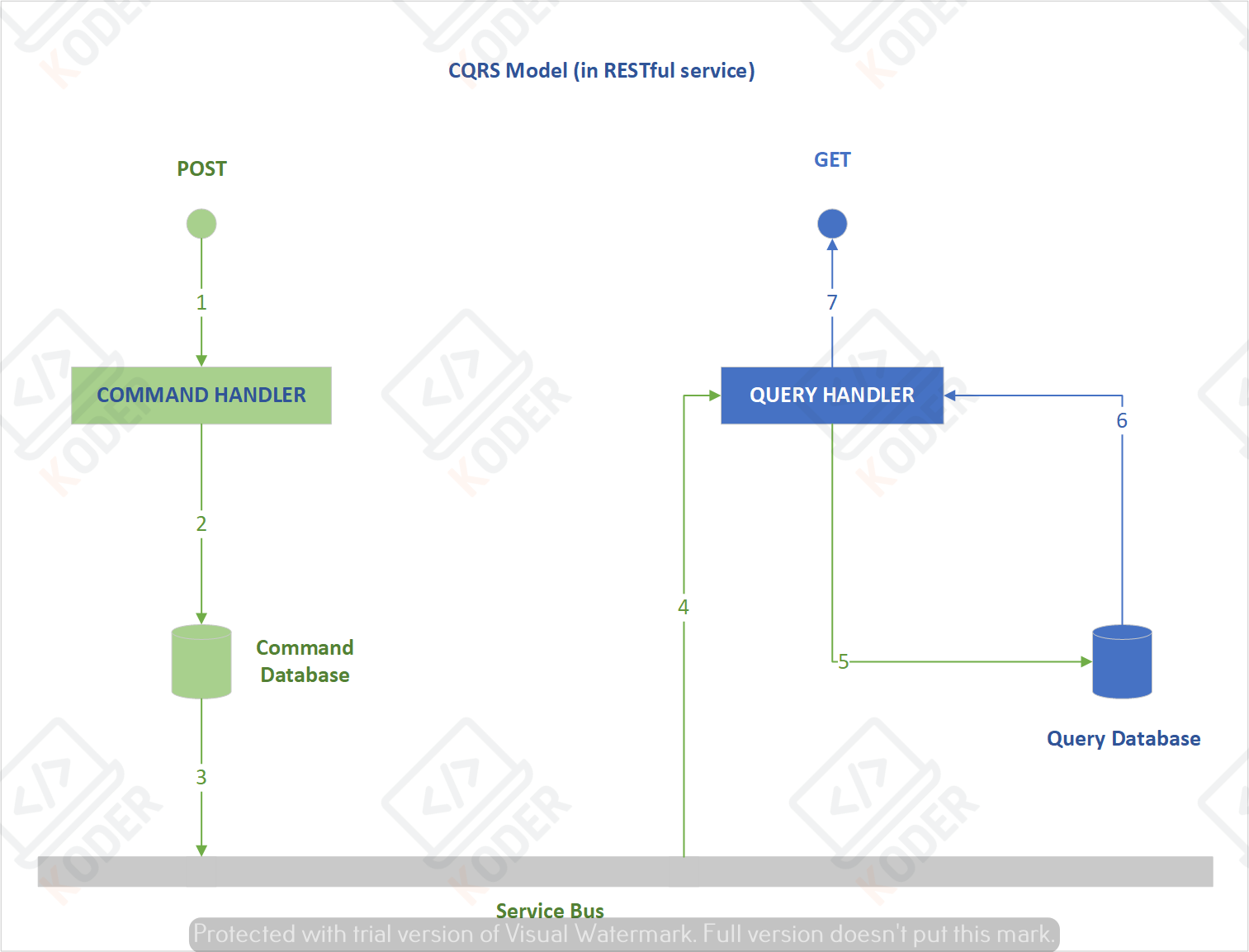
Giả sử ta triển khai app theo pattern CQRS, khi này một đối tượng Product sẽ được lưu trữ và truy xuất dữ liệu tại hai database khác nhau, một cho đọc (query) và một cho ghi (command)
Cấu hình thư viện
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-r2dbc'
implementation 'org.postgresql:r2dbc-postgresql'Cấu hình thông tin kết nối thông qua file YAML
spring:
r2dbc:
product:
driver: postgresql
host: ${POSTGRESQL_COMMAND_HOST}
port: ${POSTGRESQL_COMMAND_PORT}
database: ${APP_PRODUCT_DATABASE}
username: ${POSTGRESQL_COMMAND_USERNAME}
password: ${POSTGRESQL_COMMAND_PASSWORD}
query:
driver: postgresql
host: ${POSTGRESQL_QUERY_HOST}
port: ${POSTGRESQL_QUERY_PORT}
database: ${APP_PRODUCT_QUERY_DATABASE}
username: ${POSTGRESQL_QUERY_USERNAME}
password: ${POSTGRESQL_QUERY_PASSWORD}Tạo các file cấu hình đọc cấu hình kết nối này
@Configuration
@EnableR2dbcRepositories(
basePackages = "com.etask.product.domain.product.infrastructure.repository.product", // #1
entityOperationsRef = "productR2dbcEntityTemplate" // #2
)
@Slf4j
public class ProductDatabaseConfig {
@Value("${spring.r2dbc.product.host}")
private String host;
@Value("${spring.r2dbc.product.port}")
private int port;
@Value("${spring.r2dbc.product.database}")
private String database;
@Value("${spring.r2dbc.product.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${spring.r2dbc.product.password}")
private String password;
@Primary
@Bean
public ConnectionFactory productConnectionFactory() { // #3
ConnectionFactoryOptions options = ConnectionFactoryOptions.builder()
.option(ConnectionFactoryOptions.DRIVER, "postgresql")
.option(ConnectionFactoryOptions.HOST, host)
.option(ConnectionFactoryOptions.PORT, port)
.option(ConnectionFactoryOptions.DATABASE, database)
.option(ConnectionFactoryOptions.USER, username)
.option(ConnectionFactoryOptions.PASSWORD, password)
.option(ConnectionFactoryOptions.SSL, true)
.option(Option.valueOf("sslMode"), "prefer") // Use 'require' instead of 'prefer'
.option(Option.valueOf("connectTimeout"), "5000") // 5 seconds timeout
.build();
return ConnectionFactories.get(options);
}
@Primary
@Bean
public R2dbcEntityTemplate productR2dbcEntityTemplate( // #4
@Qualifier("productConnectionFactory") ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
return new R2dbcEntityTemplate(connectionFactory);
}
}#1 chỉ định package cho repository
#2 tên của method cấu hình khi muốn sử dụng thông qua R2dbcEntityTemplate, kết nối đến DB qua template là một cách khác bên cạnh việc sử dụng repository.
#3 cấu hình kết nối đến database, ConnectionFactory là một Bean được sử dụng bở Repository
#4 cấu hình cho việc sử dụng R2dbcEntityTemplate, ở đây ta thấy có dùng annonation @Qualifier(“productConnectionFactory”), tức là nó sẽ sử dụng cấu hình của Bean productConnectionFactory thay cho cấu hình mặc định.
Các file repository
Với cấu hình này ta sẽ phải tạo ra 2 repository tương ứng cho Command và Query, và trong file cấu hình ta thấy có chỉ định package cho repo, do vậy ta phải tách hai repo ở 2 package khác nhau
├── repository
│ ├── product
│ │ └── ProductRepository.java
│ └── query
│ └── ProductQueryRepository.javaMongoDB
Giả sử app của ta cần kết nối đến CSDL MongoDB để lưu trữ dữ liệu về Auditting, kết nối đến MongoDB có yêu cầu sử dụng SSL và xác thực qua Certificate file để đảm an toàn.
Các CDSL thường đưa ra một CA file
.crtđể cho client (app) có thể xác thực được kết nối đến database, trong JVM trong Java sẽ không thể xác thực bằng file.crtdo vậy ta cần convert.crtsang dạng mà JVM hỗ trợ làtruststorefile. Mọi người tìm hiểu thêm để biết cách convert.
File truststore.jks có thể đặt ở thư mục resource của app trong quá trình phát triển, file này nên được quản lý bở các service chuyên biệt.
Cấu hình thư viện
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb-reactive'Cấu hình thông tin kết nối trong YAMl file
Mật khẩu của truststore file được thiết lập khi chuyển .crt sang .jks
spring.data.mongodb.uri: mongodb://${MONGO_CLUSTER_USER}:${MONGO_CLUSTER_PASSWORD}@{MONGO_CLUSTER_ENPOINTS}/etaskdb?replicaSet=rs0&authSource=etaskdb&tls=true
mongodb.ssl.truststore-password: ${MONGO_CLUSTER_SSL_PASSWORD}File cấu hình trong App
Trong file cấu hình này ta để ý đến
@Configuration
public class MongoSslConfig {
@Value("${spring.data.mongodb.uri}")
private String mongoUri;
@Value("${mongodb.ssl.truststore-password}")
private String sslPass;
@Bean
public MongoClient mongoClient() throws Exception {
// Load truststore from resources
KeyStore trustStore = KeyStore.getInstance("JKS");
try (InputStream is = getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("truststore.jks")) { // #1
if (is == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("truststore.jks not found in classpath");
}
trustStore.load(is, sslPass.toCharArray());
}
// Create SSLContext with truststore
SSLContext sslContext = SSLContexts.custom() // #2
.loadTrustMaterial(trustStore, null)
.build();
// Configure MongoClient to use custom SSLContext
MongoClientSettings settings = MongoClientSettings.builder()
.applyConnectionString(new ConnectionString(mongoUri))
.applyToSslSettings(builder -> builder.enabled(true).context(sslContext)) // #3
.build();
return MongoClients.create(settings);
}
}Trong file cấu hình này ta để ý một số điểm sau
#1 load file truststore.jks, như trong đoạn code trên là đang được load từ resource folder
#2 tạo SSL context #3 đưa SSL context vào cấu hình kết nối với MongoDB
Ta có thể sử dụng Mongo qua MongoRepository hoặc thông qua template ReactiveMongoTemplate
Elasticsearch
ElasticSearch được sử dụng hiệu quả khi xây dựng hàm tìm kiếm bở việc nó hỗ trợ nhiều loại toán tử tìm kiếm, trọng số kết quả tìm kiếm, và trong thời gian gần đây với phiên bản 8.x nó đã hỗ trợ việc lưu trữ dạng Vector do vậy rất hiệu quả sử dụng embedding dữ liệu để hỗ trợ các AI model.
Elasticsearch hiện cũng đã hỗ trợ kết nối kiểu reactive, giả sử ta cần kết nối với Elasticsearch thông qua SSL và có xác thực bở Certificate, và sử dụng API key.
Cấu hình thư viện
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-r2dbc'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch'
implementation 'org.springframework.data:spring-data-elasticsearch'Cấu hình YAML file
spring:
elasticsearch:
api-key: ${ELASTIC_API_KEY}
custom-uris: ${ELASTIC_API_ENDPOINT:elasticsearch:9200}
ssl-pass: ${ELASTIC_SSL_PASS}
connection-timeout: 5s
socket-timeout: 3sCấu hình thông trong Java
@Configuration
public class ElasticsearchProductConfig {
@Value("${spring.elasticsearch.custom-uris}")
private String elasticsearchUrl;
@Value("${spring.elasticsearch.api-key}")
private String secretKey;
@Value("${spring.elasticsearch.ssl-pass}")
private String sslPass;
@Bean
public ClientConfiguration clientConfiguration() throws Exception {
KeyStore trustStore = KeyStore.getInstance("JKS");
try (InputStream is = getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("truststore.jks")) {
if (is == null) {
throw new FileNotFoundException("truststore.jks not found in classpath");
}
trustStore.load(is, sslPass.toCharArray());
}
SSLContext sslContext = SSLContexts.custom()
.loadTrustMaterial(trustStore, null)
.build();
return ClientConfiguration.builder()
.connectedTo(elasticsearchUrl)
.usingSsl(true)
.withConnectTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(5))
.withSocketTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(3))
.withDefaultHeaders(getDefaultHeaders())
.withClientConfigurer(ElasticsearchClients.ElasticsearchHttpClientConfigurationCallback.from(
httpAsyncClientBuilder -> httpAsyncClientBuilder
.setSSLContext(sslContext)
.setMaxConnTotal(100)
.setMaxConnPerRoute(100)
.setKeepAliveStrategy((response, context) -> Duration.ofMinutes(2).toMillis())
))
.build();
}
private HttpHeaders getDefaultHeaders() {
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.add("Content-Type", MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE);
headers.add("Accept", MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE);
headers.add("Authorization", "ApiKey " + secretKey); // #1
return headers;
}
@Bean
public ReactiveElasticsearchClient reactiveElasticsearchClient() throws Exception { // #2
return ElasticsearchClients.createReactive(clientConfiguration());
}
@Bean
public ReactiveElasticsearchTemplate reactiveElasticsearchTemplate( // #3
ReactiveElasticsearchClient client) {
return new ReactiveElasticsearchTemplate(client,
new MappingElasticsearchConverter(
new SimpleElasticsearchMappingContext()
));
}
}Trong cấu hình Elasticsearch sử dụng truststore tương tự như Mongo khi ta tạo một SSL context, ta để ý đến một số cấu hình sau
#1 kết nối qua API key đặt trong header, nếu cấu hình qua Username/Password ta thay bằng Basic Auth và truyển username/password #2 ReactiveElasticsearchClient tạo một Bean cho client, cấu hình này được sử dụng khi dùng ReactiveElasticsearchRepository #3 ReactiveElasticsearchTemplate cấu hình sử dụng qua template
Ví dụ về sử dụng qua template
private final ReactiveElasticsearchTemplate elasticsearchTemplate;
public Mono<Page<ProductResponse>> searchProducts(String name, Double minPrice, Double maxPrice, Pageable pageable) {
Query multiMatch = MultiMatchQuery.of(m -> m
.fields("name", "description")
.query(name)
.analyzer("standard")
)._toQuery();
Query priceRange = RangeQuery.of(
r -> r.number(nv ->
nv.field("price")
.gte(minPrice)
.lte(maxPrice))
)._toQuery();
Query boolQuery = BoolQuery.of(b -> b
.must(multiMatch)
.filter(priceRange)
)._toQuery();
NativeQuery searchQuery = NativeQuery.builder()
.withQuery(boolQuery)
.withPageable(pageable)
.build();
return elasticsearchTemplate.search(searchQuery, ProductIndex.class)
.collectList()
.as(flux -> databaseRetryUtil.applyRetry(flux, "search products in elasticsearch", log))
.map(hits -> {
List<ProductResponse> products = hits.stream()
.map(SearchHit::getContent)
.map(productMapper::mapToResponse)
.toList();
long total = hits.size();
return new PageImpl<>(products, pageable, total);
});
}Redis
Trong một số bài viết về Gateway chúng ta đã biết Redis có thể dùng để hỗ trợ cho cơ chế ratelimit. Redis ngoài ra còn có rất nhiều các ứng dụng khác nhau.
Giả sử ta có yêu cầu lưu sử dụng Redis cho lưu trữ cached của ứng dụng, kết nối đến Redis sử dụng username/password và xác thực kết nối qua certificate file (.crt) ta sẽ cấu hình kết nối như sau
Cấu hình thư viện
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-redis-reactive'Yaml file
spring:
data:
redis:
host: ${REDIS_HOST:redis}
port: ${REDIS_PORT:6379}
database: 0
password: ${REDIS_PASSWORD}
username: ${REDIS_USERNAME:default}
ssl:
enabled: ${REDIS_SSL_ENABLED:false}Java file
Tại SslOption ta có thể load trực tiếp certificate file (.crt), hơi khác một chút với kết nối sử dụng truststore file như trong Mongo hoặc ElastisSearch.
public class RedisConfig {
private final ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
@Value("${spring.data.redis.host:localhost}")
private String host;
@Value("${spring.data.redis.port:6379}")
private int port;
@Value("${spring.data.redis.password:}")
private String password;
@Value("${spring.data.redis.username}")
private String username;
@Bean
public LettuceConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory() throws IOException {
RedisStandaloneConfiguration redisStandaloneConfiguration = new RedisStandaloneConfiguration();
redisStandaloneConfiguration.setHostName(host);
redisStandaloneConfiguration.setPort(port); // Or your SSL port, usually 6380 or custom
redisStandaloneConfiguration.setPassword(password); // If your Redis requires authentication
redisStandaloneConfiguration.setUsername(username);
LettuceClientConfiguration.LettuceClientConfigurationBuilder lettuceClientConfigurationBuilder = LettuceClientConfiguration.builder();
// Enable SSL
lettuceClientConfigurationBuilder.useSsl();
SslOptions sslOptions = SslOptions.builder()
.trustManager(resourceLoader.getResource("classpath:redis.crt").getFile())
.build();
ClientOptions clientOptions = ClientOptions.builder()
.sslOptions(sslOptions)
.build();
lettuceClientConfigurationBuilder.clientOptions(clientOptions);
LettuceClientConfiguration lettuceClientConfiguration = lettuceClientConfigurationBuilder.build();
return new LettuceConnectionFactory(redisStandaloneConfiguration, lettuceClientConfiguration);
}
}Lưu ý khi muốn sử dụng ReactiveRedisTemplate đẻ lưu một đối tượng POJO trong Java ta cần cấu hình thêm một serializer để template có thể hiều để chuyển Java Object sang Object trong Redis và ngược lại
public class RedisTemplateConfig {
private final ObjectMapper objectMapper;
@Bean
public ReactiveRedisTemplate<String, ProductResponse> reactiveRedisTemplate(
ReactiveRedisConnectionFactory factory) {
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<ProductResponse> serializer =
new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(ProductResponse.class);
serializer.setObjectMapper(objectMapper);
RedisSerializationContext.RedisSerializationContextBuilder<String, ProductResponse> builder =
RedisSerializationContext.newSerializationContext(new StringRedisSerializer());
RedisSerializationContext<String, ProductResponse> context =
builder.value(serializer).build();
return new ReactiveRedisTemplate<>(factory, context);
}
}Đây là một đoạn code ví dụ về sử dụng reativeTemplate, ta thấy có một số toán tử được sử dụng ở đây như set, as, doOnSuccess và then
return reactiveRedisTemplate.opsForValue()
.set(key, productResponse, CACHE_TTL)
.as(mono -> applyRetry(mono, "save"))
.doOnSuccess(aVoid -> log.info("Product saved to cache: {}", productResponse.uuid()))
.then();WebClient
Trong Spring MVC ta có thể dụng RestTemplate khi muốn kết nối đến các hệ thống khác qua HTTP Request, khi làm việc với Reactive trong WebFlux có một thư viện khác tương đương là WebClient, cách sử dụng như thế nào mình sẽ giới thiệu ở bên dưới. Có một điều đặc biệt là ngày nay trong một số dự án bằng Spring MVC (none reactive) nhưng các developer cũng sử dụng WebClient cho việc gọi HTTP Request thay cho RestTemplate truyền thống, vì một số ưu điểm của nó:
- Khả năng gọi lại (retry)
- Mapping response
- Khả năng điều khiển lỗi
Để sử dụng WebClient ta có thể sử dụng trực tiếp không cần cấu hình, nhưng khi chúng ta làm việc với các hệ thống Tracing (Micrometer), thì WebClient được yêu cầu thêm tạo cấu hình
@Configuration
public class HttpClientConfig {
@Bean
public WebClient webClient(WebClient.Builder builder) {
return builder.build(); // Spring will inject a builder with tracing filters
}
}Đây là một ví dụ sử dụng WebClient, ta thấy có sử dụng cơ chế retry ở toán tử as mà ta đã tìm hiểu trong bài trước, thông báo khi gọi API thành công, và xử lý lỗi khi gọi thất bại onErrorResume
private final WebClient webClient;
private Mono<ProductResponse> fetchFromCache(String uri, String uuid) {
return webClient.get().uri(uri + uuid)
.retrieve()
.bodyToMono(ProductResponse.class)
.onErrorResume(WebClientResponseException.class, ex -> {
if (ex.getStatusCode().is4xxClientError()) {
if (ex.getStatusCode().value() == 404) {
log.info("Product not found in cache (404) for uuid: {}", uuid);
return Mono.error(new ProductNotFoundInCachedException("Product not found in cache"));
}
// Handle other 4xx errors as needed
log.warn("Client error fetching from cache: {} for uuid: {}", ex.getStatusCode(), uuid);
return Mono.error(new CachedSystemException(ex.getMessage()));
}
return Mono.error(new CachedSystemException(ex.getMessage()));
})
.as(mono -> databaseRetryUtil.applyRetry(mono, "fetch product from cache", log))
.doOnSuccess(response -> log.info("Fetched product from cache: {}", response));
}Lưu trữ file lên hệ thống S3 với Reactive
Trong các ứng dụng của chúng ta việc lưu trữ file cũng là nghiệp vụ thường xuyên được sử dụng, vậy lưu trữ theo cơ chế reative như thế nào, chúng ta hãy cùng tìm hiểu.
S3 (Simple Storage Service) được một số nhà cung cấp dịch vụ hỗ trợ như Amazon S3, Wasabi, chúng ta cũng có thể tự xây dựng cho mình hệ thống file lưu trữ theo kiểu S3 bằng cách sử dụng
MinIO
Cấu hình thư viện
implementation 'software.amazon.awssdk:s3:2.31.59'
implementation 'software.amazon.awssdk:netty-nio-client:2.31.59'Cấu hình S3AsyncClient
public S3AsyncClient s3AsyncClient() {
return S3AsyncClient.builder()
.endpointOverride(URI.create(endpoint))
.region(Region.of(region))
.credentialsProvider(StaticCredentialsProvider.create(
AwsBasicCredentials.create(accessKey, secretKey)))
.build();
}Cách sử dụng S3Client
private final S3AsyncClient s3Client;
s3Client.putObject(req -> req
.bucket(bucketName)
.key(s3Key)
.contentType(filePart.headers().getContentType() != null ?
filePart.headers().getContentType().toString() : "application/octet-stream")
.build(),
AsyncRequestBody.fromBytes(bytes))Tổng kết
Để ứng dụng reactive phát huy được khả năng non-blocking thì có yêu cầu là kết nối reactive qua các dịch vụ đều là reactive (end-to-end), hiều và nắm bắt được việc cấu hình để kết nối các dịch vụ là rất quan trọng. Các dịch vụ kết nối ở trên là rất cơ bản, trong khi phát triển các ứng dụng của mình có thể có những dịch vụ khác mọi người tìm hiểu thêm.
Một ứng dụng viết dưới dạng reactive, kết hợp với sử dụng các kỹ thuật như Virtual Thread và build app dưới dạng native sử dụng GraalVM cũng sẽ làm tăng đáng kể hiệu năng hệ thống trong một tài nguyên hữu hạn.

Related Posts