Event Sourcing
Giả sử ta có dữ liệu tài khoản của một người như sau, vậy để tính số tài khoản hiện tại ta tổng hợp từ sự kiện theo dòng thời gian của tài khoản
+--------+-----------+-----------+---------+------------+
| userId | eventType | amount | version | date |
+--------+-----------+-----------+---------+------------+
| khoavu | INIT | 1.000.000 | 1 | 01-01-2025 |
+--------+-----------+-----------+---------+------------+
| khoavu | WITHDRAW | 500.000 | 2 | 02-01-2025 |
+--------+-----------+-----------+---------+------------+
| khoavu | DEPOSITE | 300.000 | 3 | 03-01-2025 |
+--------+-----------+-----------+---------+------------+currentMount = 1.000.000 - 500.000 + 300.000 = 800.000
Event sourcing là một pattern với ý tưởng lưu trữ toàn bộ các sự kiện (event) có tác động thay đổi trạng thái (state) của đối tượng, khi cần truy vấn trạng thái hiện tại của đối tượng, hệ thống sẽ tổng hợp (aggregate/ hoặc replay) từ các sự kiện của đối tượng đó theo đúng thứ tự đã diễn ra của sự kiện.
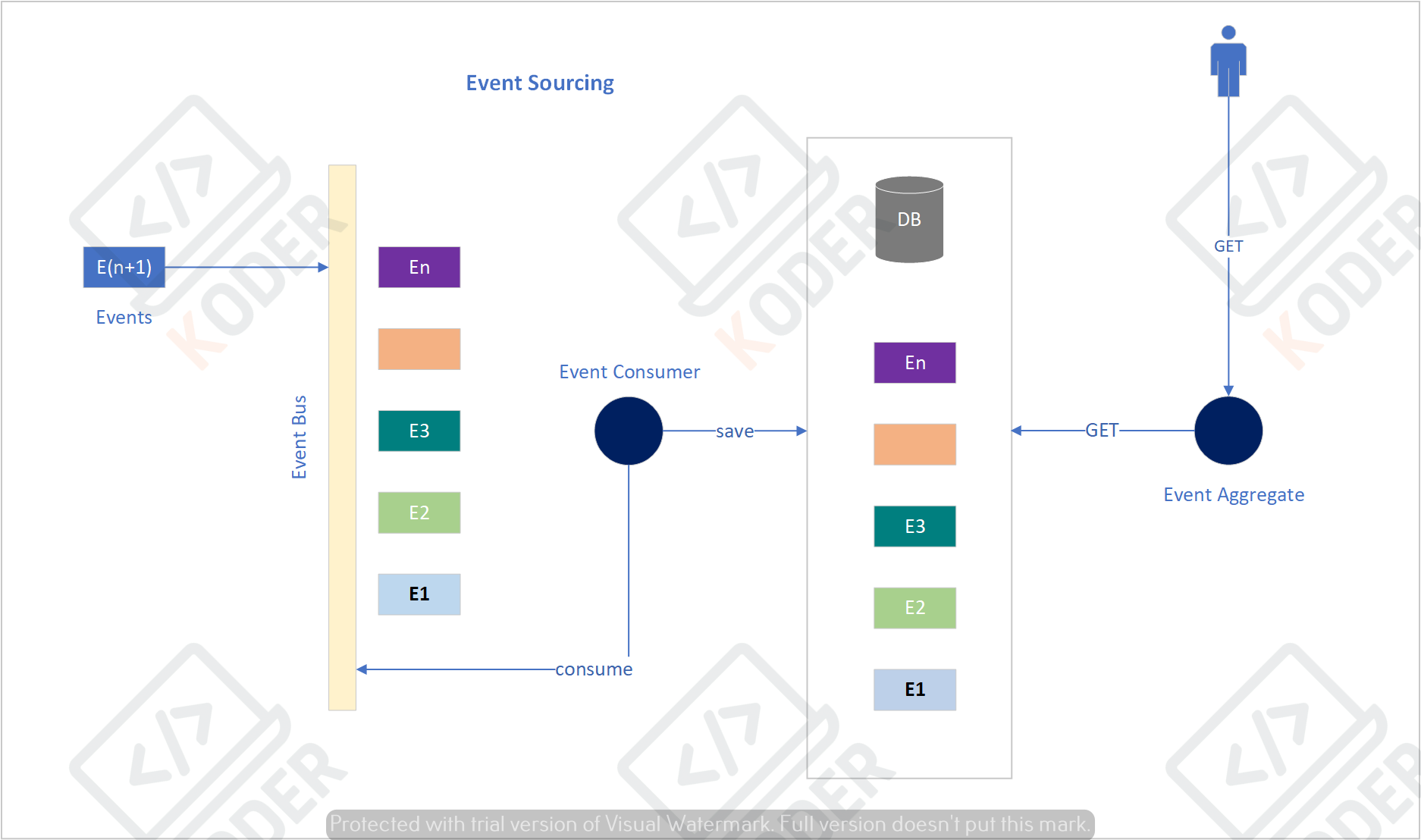
Trong sơ đồ tuần tự trên mô tả cách triển khai theo mô hình event sourcing
Event là một sự kiện sảy ra với đối tượng
Với đối tượng là tài khoản thì các sự kiện sảy ra như: INIT, WITHDRAW, DEPOSITE…, với các đối tượng như Kho bãi thì các sự kiện như: ORDER, RESERVED, INCREASED, DECREASED
Event Bus
Các sự kiện sẽ được đẩy vào Event Bus, trong quá trình imlement thực tế sẽ sử dụng các hệ thống quản như Kafka, RabitMQ để lưu nhận các Event message
Event Consumer
Lắng nghe các event được gửi vào Event Bus, sau đó lưu trữ vào database, Event Consumner phải đảm bảo các sự kiện lưu đúng theo thứ tự đã diễn ra, như ta đã biết khi lưu trữ dữ liệu vào trong database sẽ có thể sảy ra hiện tượng racing condition mình sẽ trình bày cách xử lý racing condition vào một bài khác.
Event Aggregate
Khi có yêu cầu truy vẫn dữ liệu như kiểm tra số dư tài khoản hiện tại, tồn kho, sẽ dựa vào các hàm tổng hợp (aggregate) để tính ta được dữ liệu yêu cầu
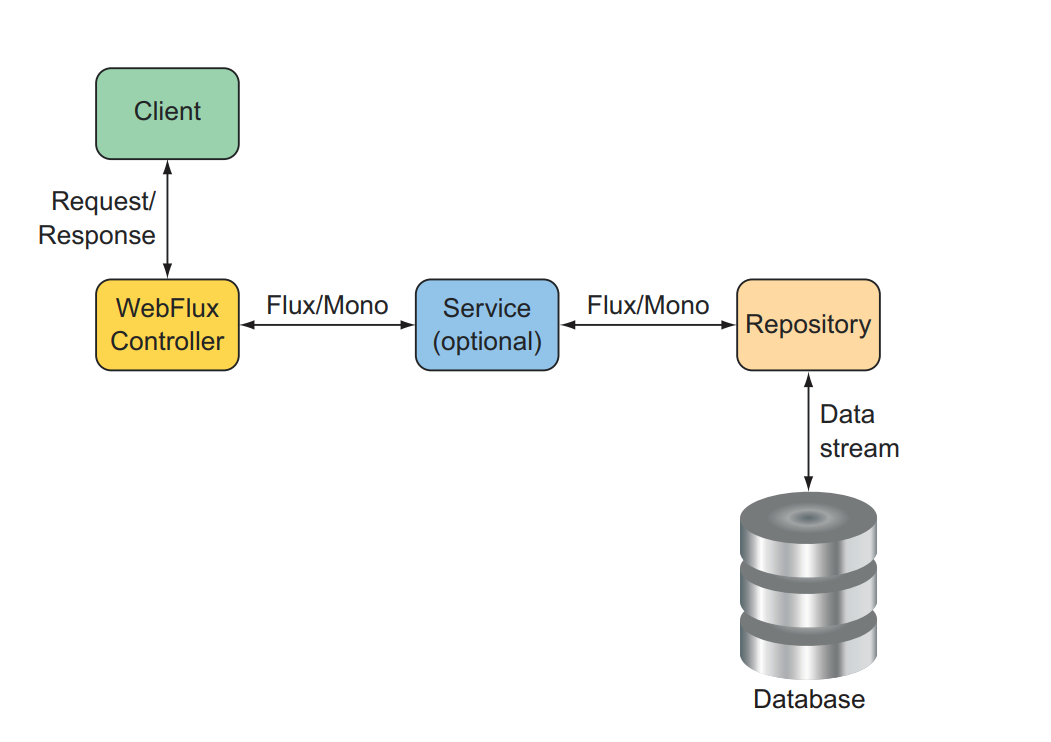
Event Sourcing có thể kết hợp với pattern CQRS, khi Event Sourcing được implement ở Query layer.
Một số class chính khi triển khai Event Sourcing cho đối tượng Account
Giả sử ta có một ứng dụng đặt hàng Order, khi có một order được yêu cầu, hệ thống sẽ gửi Order này vào Event Bus (Kafka), service Payment nơi chứa đối tượng Account sẽ lắng nghe được Order này và tiến hành ghi các sự kiện vào trong tài khoản
- Nếu tài khoản đủ ghi mã sự kiện là HOLD (tạm giữ amount này)
Đoạn code bên dưới được tách ra từ một dự án có triển khai SAGA (mà mình sẽ giới thiệu sau), có một vài đoạn như cần xử lý HOLD, UN_HOLD account, các bạn chưa cần quan tâm đến chỗ này, chỉ cần để ý đến luồng ghi một Event vào trong database.
AccountEntity thực thể lưu trữ đối tượng Account trong database
public record AccountEntity(
@Id
Long id,
String refId,
AccountReferenceType accountReferenceType,
String customerId,
BigDecimal initialBalance,
BigDecimal amount,
AccountEventType eventType,
Long version,
Instant createdAt) {}AccountEventType loại sự kiện, dựa vào loại sự kiện này khi tổng hợp tài khoản ta sẽ cộng tại khoản khi INIT, UN_PAY, DEPOSIT, UN_HOLD và trừ tài khoản khi PAY, WITHDRAW, ON_HOLD
public enum AccountEventType {
INIT, // Khởi tạo
PAY, // Thanh toán
UN_PAY, // Hủy thanh toán
WITHDRAW, // Rút tiền
DEPOSIT, // Nạp tiền
ON_HOLD, // Tạm giữ
UN_HOLD // Hủy tạm giữ
}version là số thứ tự đảm bảo khi tổng hợp các sự kiện diễn ra đúng thứ tự
Account là model thể hiện giá trị tổng hợp, đầu vào là một Danh sách sự kiện List<AccountEntity>, sau đó dựa vào loại sự kiện ta tổng hợp được giá trị hiện tại của tài khoản.
@Getter
@AllArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PRIVATE)
public class Account {
private String customerId;
private BigDecimal balance;
private long version;
private Instant lastUpdatedAt;
public static Account from(List<AccountEntity> accountEntities) {
if (accountEntities.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot create Account from empty accountEntities");
}
AccountEntity createEvent = accountEntities.stream()
.filter(accountEntity -> accountEntity.eventType() == AccountEventType.INIT)
.findFirst()
.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("No account creation event found"));
String customerId = createEvent.customerId();
BigDecimal balance = createEvent.initialBalance();
AtomicReference<Instant> lastUpdated = new AtomicReference<>(createEvent.createdAt());
balance = accountEntities.stream()
.filter(accountEntity -> accountEntity.eventType() != AccountEventType.INIT)
.peek(accountEntity -> lastUpdated.set(accountEntity.createdAt()))
.reduce(balance, (currentBalance, accountEntity) -> switch (accountEntity.eventType()) {
case PAY, WITHDRAW, ON_HOLD -> currentBalance.subtract(accountEntity.amount()); //#1 cộng
case UN_PAY, DEPOSIT, UN_HOLD -> currentBalance.add(accountEntity.amount()); //#2 trừ
default -> currentBalance;
}, BigDecimal::add);
return new Account(customerId, balance, accountEntities.size(), lastUpdated.get());
}
}#1 cộng với các loại sự kiện PAY, WITHDRAW, ON_HOLD.
#2 trừ với các loại sự kiện UN_PAY, DEPOSIT, UN_HOLD
PaymentConsumerService là Event Consumer, nó lắng nghe các sự kiện sau đó gọi hàm lưu vào trong cơ sở dữ liệu, service accountPaymentAction.handle(event) đảm bảo “nếu được lưu thành công sẽ lưu đúng thứ tự”
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Slf4j
public class PaymentConsumerService {
private final AccountPaymentAction accountPaymentAction;
private final StreamBindingsProperties properties;
@Bean
public Function<KStream<String, OrderEvent>, KStream<String, OrderEvent>> paymentOrders() {
return this::processPaymentOrders;
}
private KStream<String, OrderEvent> processPaymentOrders(KStream<String, OrderEvent> inputStream) {
// Process the events and store the resulting stream
KStream<String, OrderEvent> processedStream = inputStream
.peek((key, event) -> log.info("Received payment event for processing: key={}, event={}", key, event))
.mapValues(event -> {
log.info("Handling payment for event: {}", event);
OrderEvent result = accountPaymentAction.handle(event).block(); //#1 Save to Database
assert result != null;
if (result.eventStatus() == OrderEventStatus.REJECT) {
result = result.withRejectedServices(List.of(OrderEventService.ACCOUNT_SERVICE));
}
log.info("Result after handling payment: {}", result);
return result;
});
// Branch the stream based on event status
KStream<String, OrderEvent>[] branches = processedStream.branch(
(key, value) -> value.eventStatus() == OrderEventStatus.ACCEPTED
|| value.eventStatus() == OrderEventStatus.ACCEPTED_FAILED,
(key, value) -> value.eventStatus() == OrderEventStatus.REJECTED ||
value.eventStatus() == OrderEventStatus.REJECTED_FAILED,
(key, value) -> value.eventStatus() == OrderEventStatus.ACCEPT ||
value.eventStatus() == OrderEventStatus.REJECT
);
// Send each branch to the appropriate topic
branches[0].to(properties.getPaymentOrdersOut0().getDestination());
branches[1].to(properties.getPaymentOrdersOut1().getDestination());
branches[2].to(properties.getPaymentOrdersOut2().getDestination());
return processedStream.filter((k, v) -> false);
}
}//#1 Save to Database đây là một interface để lưu trữ dữ liệu vào Database, interface được implment bởi service AccountPaymentActionFacade
public class AccountPaymentActionFacade implements AccountPaymentAction {
private final AccountDatabase accountDatabase;
@Override
public Mono<OrderEvent> handle(OrderEvent orderEvent) {
return switch (orderEvent.eventStatus()) {
case INIT -> accountDatabase.holdAmountOrder(orderEvent); //#1. Lưu trữ vào cơ sở dữ liệu
case ACCEPT -> accountDatabase.payOrder(orderEvent);
case REJECT -> orderEvent.rejectedServices().contains(OrderEventService.ACCOUNT_SERVICE)
? Mono.just(orderEvent.withEventType(OrderEventStatus.REJECTED))
: accountDatabase.unPayOrder(orderEvent);
default -> Mono.just(orderEvent);
};
}
}Ta hãy xem hàm holdAmountOrder trong AccountDatabase hoạt động như thế nào
AccountDatabaseAdaptor là một implement của AccountDatabase, trong hàm này ta để ý đến method attemptToPay, đây là một method tính toán giá trị cần thanh toán, nếu tài khoản không đủ thì trả về fail, nếu tài khoản đủ thì tạo sự kiện ON_HOLD
private Mono<Boolean> attemptToPay(Order order, AccountEventType accountEventType) {
return accountRepository.findByCustomerIdOrderByVersion(order.customerId())
.collectList()
.flatMap(accounts -> {
if (accounts.isEmpty()) {
log.info("No account found for customerId: {}", order.customerId());
return Mono.just(false);
}
BigDecimal totalCost = getCostFromOrder(order);
Account account = Account.from(accounts); // #1 Tổng hợp giá trị hiện tại của account
long expectedVersion = account.getVersion() + 1;
if (account.getBalance().compareTo(totalCost) < 0) {
log.info("Insufficient balance for customerId: {}", order.customerId());
return Mono.just(false);
}
AccountEntity entity =
AccountEntity.createNewForOrder(
order.uuid(),
order.customerId(),
totalCost,
accountEventType,
expectedVersion);
return accountRepository.findByCustomerIdAndVersion(order.customerId(), expectedVersion)
.hasElements()
.flatMap(exist -> {
if (exist) {
log.info("Version conflict detected for customerId: {}", order.customerId());
return Mono.error(new AccountVersionConflictException("Version conflict detected for customerId: " + order.customerId()));
}
return accountRepository.save(entity.withEventType(accountEventType)) // #2 Tổng hợp giá trị hiện tại của account
.doOnSuccess(saved -> log.info("Account updated successfully for customerId: {}", order.customerId()))
.thenReturn(true)
.onErrorResume(e -> {
log.error("Error saving account for customerId: {}", order.customerId(), e);
return Mono.error(new AccountSaveException("Error saving account for customerId: " + order.customerId(), e));
});
});
});
}#1 Tổng hợp giá trị account
#2 Lưu sự kiện vào database
Tổng kết
Event Sourcing có thể không cần thiết cho các đối tượng CRUD đơn giản nhưng khi hệ thống yêu cầu về khả năng truy vết (traceability) hay Ai đã làm những gì (auditability), hoặc kiểm tra xem trạng thái/giá trị của một đối tượng ở một thời điểm bất kỳ trong quá khứ, hoặc trong hệ thống triển khai Microservice theo mô hình event-driven thì việc triển khai Event Sourcing sẽ cần thiết.
Event Sourcing thường kết hợp với CQRS để cho hiệu năng tối ưu.
Có nhiều cách triển khải Event Sourcing, đoạn code trên chỉ là một ví dụ khi triển khai Spring Boot theo mô hình Microservice.
Source code các bạn có thể tham khảo tại đây

Related Posts